Over 44 million people in the US suffer from a mental disorder, causing many many problems for them and their families. Yet less than half of people with mental illness get treatment (SAMHSA/NIH report, January 2018).
Individualized Treatment for Mental Illness and Dual-Disorders
Mental illness is defined as a mental, behavioral, or emotional disorder using criteria from DSM 5. Serious mental illness is defined as one of these resulting in functional impairment, which majorly interferes with or limits one or more major life activities.
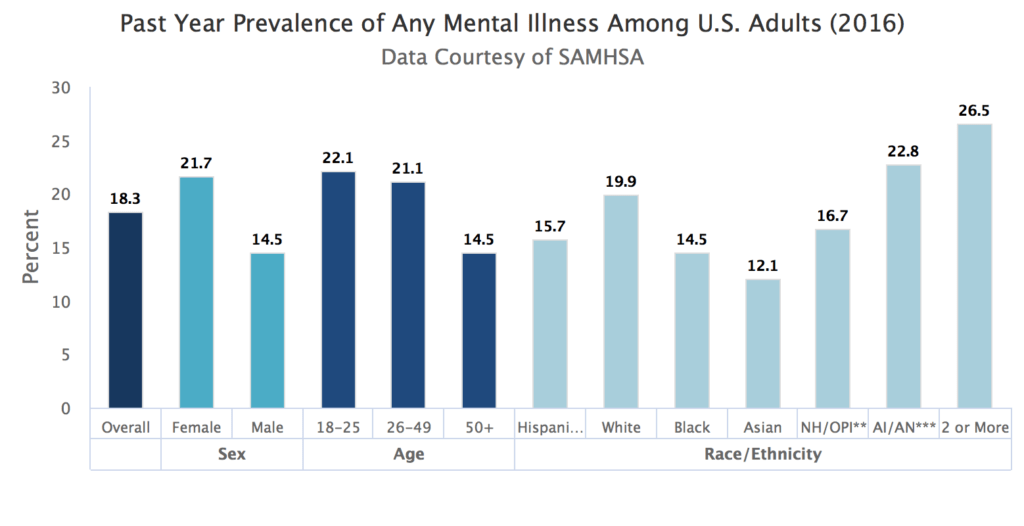
What the Chart Says
- In 2016, there were an estimated 44.7 million adults aged 18 or older in the United States with AMI. This number represented 18.3% of all U.S. adults.
- The prevalence of AMI was higher among women (21.7%) than men (14.5%).
- Young adults aged 18-25 years had the highest prevalence of AMI (22.1%) compared to adults aged 26-49 years (21.1%) and aged 50 and older (14.5%).
- The prevalence of AMI was highest among the adults reporting two or more races (26.5%), followed by the American Indian/Alaska Native group (22.8%). The prevalence of AMI was lowest among the Asian group (12.1%).